Java Thread Safe
Java Thread Safe
thread safe
- 여러 쓰레드에서 동시에 공유자원에 접근할 때, 안정성이 보장되는 것
synchronized
하나의 객체 혹은 공용 객체에 여러 객체가 동시에 접근하여 데이터를 조작하는 상황에서 사용하는 동기화 키워드며 lock을 걸어 동기화를 수행한다.
synchronized가 적용된 객체 혹은 메서드는 하나의 쓰레드만 접근할 수 있고 접근을 시도하는 다른 쓰레드는 block 상태가 된다.
또, 생성자를 동기화할 수 없다.
Note that constructors cannot be synchronized — using the synchronized keyword with a constructor is a syntax error. Synchronizing constructors doesn’t make sense, because only the thread that creates an object should have access to it while it is being constructed.
- 종류
- method 방식
- block 방식
- 예를 들어, 유니세프에 기부하는 사람들이 있다. 여러 사람이 동시다발적으로 기부를 할 때 유니세프에서는 하나의 모금함을 사용한다고 하자.
- 모금함은 donation 변수이며 공유자원이다.
public class Unicef {
private int donation = 0;
public void donate() {
donation += 1000;
}
public int getDonation() {
return donation;
}
}
public class Person extends Thread {
private Unicef unicef;
private String name;
public Person(final Unicef unicef, final String name) {
this.unicef = unicef;
this.name = name;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
unicef.donate();
}
System.out.format("후원자: %s || 총 기부 금액: %s원\n", this.name, NumberFormat.getInstance().format(unicef.getDonation()));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Unicef unicef = new Unicef();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String name = "Person" + i;
new Person(unicef, name).start();
}
}
}
- 한 명의 사람은 기부를 1000번 하며, 동시에 10명이 기부를 하는 코드이다.
- 공유자원에 접근하는 메서드인 donate()에 동기화 처리가 안 되어 있는 상태에서 실행하면 어떻게 될까?
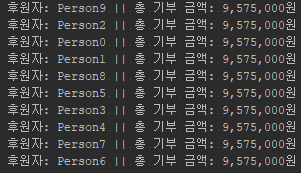
- 여러 Person 객체가 Unicef 클래스의 donate() 메소드에 동시 접근할 수 있어서 발생하는 문제이다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 동기화를 처리한다.
method 방식
public synchronized void donate() {
donation += 1000;
}
- 메소드의 반환타입 앞에 synchronized 키워드를 선언해준다. 다시 코드를 실행하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나온다.
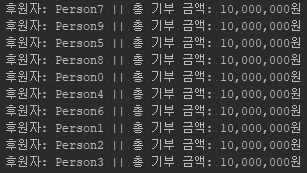
- 동기화 처리가 적용되어 동시 접근 시 공유자원에 대한 안정성이 보장된다.
메소드에 synchronized를 적용하면 같은 synchronized 메소드들은 lock이 적용된다.
public synchronized void donate() {
donation += 1000;
}
public synchronized void donate2() {
donation += 1000;
}
// 각각의 스레드가 donate(), donate2() 호출한다.
- 두 개의 동기화 메소드가 존재한다면 동시에 서로 다른 메소드를 요청해도 하나가 종료된 후에 다음 메소드를 수행한다.
- 동기화 메소드 자신의 객체에 lock을 적용한다.
block 방식
메소드 내의 동기화 블록을 사용할 수 있다.
/**
* synchronized 블록 방식
*/
public void donate() {
synchronized (this) {
donation+= 1000;
}
}
synchronized 파라미터에서 this를 주목하자.
- synchronized block에서 parameter 의미
동기화 블록 방식에서 파라미터로 this객체를 넘기는 것을 볼 수 있는데, lock을 적용할 객체를 지정한다.
아래 코드처럼 동기화 블록에서 파라미터로 this를 넘겨주었으므로 this객체가 lock을 적용할 객체가 된다.public synchronized void donate() { donation += 1000; } public void donateBlock() { synchronized (this) { donation+= 1000; } }- donateBlock() 호출 후에 donate()를 호출하더라도 같은 객체에 lock이 적용되어 있음으로 donate()는 donateBlock()가 끝날 때까지 기다린다.
- 순서를 바꾸어 donate() 호출 후에 donateBlock()을 호출해도 같은 결과가 나온다.
- synchronized 메소드만 lock처리가 되므로 일반 메소드(synchronized 없는 메소드)는 동기화와 상관없이 호출된다.
- synchronized는 Object타입을 받는데, 간단하게 new Object() 타입을 synchronized 넘겨서 실행하면 파라미터로 받은 new Object() 객체에 대해서 lock이 적용되므로 서로 다른 객체에 lock이 적용된 donateBlock(), donate()는 서로 영향을 주지 않는다.
결론
synchronized를 사용하면 공용 자원에 대해서 동기화 처리를 해주지만 lock으로 인한 성능 저하가 발생할 수 있어서 충분한 검토 후에 적용이 필요하다.

Leave a comment